Скачать с ютуб Allele-specific oligonucleotide | Immune System | Antigen | Detection | Basic Science Series в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через dTub.ru Загрузить через ClipSaver.ruСкачать бесплатно Allele-specific oligonucleotide | Immune System | Antigen | Detection | Basic Science Series в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Allele-specific oligonucleotide | Immune System | Antigen | Detection | Basic Science Series или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Allele-specific oligonucleotide | Immune System | Antigen | Detection | Basic Science Series в формате MP3:
Роботам не доступно скачивание файлов. Если вы считаете что это ошибочное сообщение - попробуйте зайти на сайт через браузер google chrome или mozilla firefox. Если сообщение не исчезает - напишите о проблеме в обратную связь. Спасибо.
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Allele-specific oligonucleotide | Immune System | Antigen | Detection | Basic Science Series
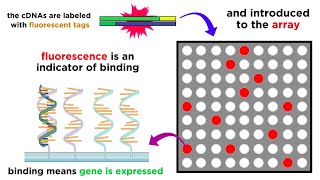
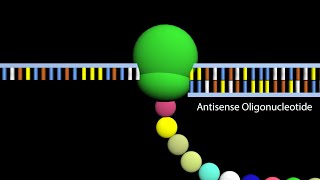
An allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) is a short piece of synthetic DNA complementary to the sequence of a variable target DNA. What is an ASO: An allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) is a short piece of synthetic DNA complementary to the sequence of a variable target DNA (Fig 1). It acts as a probe for the presence of the target DNA in a Southern blot assay or, more commonly, in the simpler Dot blot assay. It is a common tool used in genetic testing, forensics, and Molecular Biology research. (2) Structure and function of ASO: An ASO is typically an oligonucleotide of 15–21 nucleotide bases in length (Fig 2). It is designed (and used) in a way that makes it specific for only one version, or allele, of the DNA being tested. The length of the ASO, which strand it is chosen from, and the conditions by which it is bound to (and washed from) the target DNA all play a role in its specificity. (3) Mechanism of target DNA detection: These probes can usually be designed to detect a difference of as little as one base in the target's genetic sequence, a basic ability in the assay of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), important in genotype analysis and the Human Genome Project. After it has bound to its target, the ASO must be labeled with a radioactive, enzymatic, or fluorescent tag (Fig 3). (4) A specific application of an ASO: The human disease sickle cell anemia is caused by a genetic mutation in the codon for the sixth amino acid of the blood protein beta-hemoglobin. The normal DNA sequence G-A-G codes for the amino acid glutamate, while the mutation changes the middle adenine to thymine, leading to the sequence G-T-G (G-U-G in the mRNA). This altered sequence substitutes a valine into the final protein, distorting its structure (Fig 4). (5) ASO works with Southern blot and Dot blot technology: To test for the presence of the mutation in a DNA sample, an ASO probe would be synthesized to be complementary to the altered sequence as a control; another ASO would be synthesized for the normal sequence. The ASO is fully complementary to the target sequence. Using Southern blot and dot blot technology, we can detect the presence of the gene defect in any sample using specific ASO (Fig 5). Support my work at https://www.patreon.com/user?u=37177596 Twitter: / drkumarlokender Facebook: / lokenderkumar.sharma Linkedin: / dr-lokender-kumar-58525945 Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only. The content of this channel should not be considered as medical advice of any kind. Please consult your doctor for medical help. Use this information at your own risk. We hold no responsibility for any issue, concerns, or damage arising from the content of the video. Under no circumstances Basic Science Series English be responsible or liable in any way for any content, including but not limited to, any errors or omissions in the content, any loss, any damage of any kind incurred as a result of any content communicated in this video, whether by Basic Science Series English or a third party. In no event shall Basic Science Series English be liable for any special indirect or consequential damages of any damages whatsoever resulting from the content of our channel.





![[DeepLearning | видео 1] Что же такое нейронная сеть?](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/RJCIYBAAiEI/mqdefault.jpg)