Скачать с ютуб Histology of Palatine tonsil \Tonsil в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Histology of Palatine tonsil \Tonsil в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Histology of Palatine tonsil \Tonsil или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Histology of Palatine tonsil \Tonsil в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Histology of Palatine tonsil \Tonsil
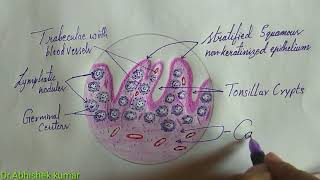
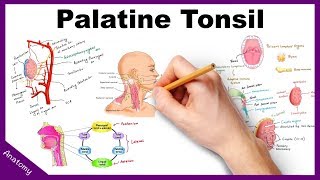
Tonsils Tonsils belong to the mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), but because they are incompletely encapsulated, they are considered organs and will be studied apart from the MALT. The tonsils constitute a lymphoid tissue that lies beneath, and in contact with, the epithelium of the initial portion of the digestive tract. Depending on their location, tonsils in the mouth and pharynx are called palatine, pharyngeal, or lingual. Palatine Tonsils The two palatine tonsils are located in the lateral walls of the oral part of the pharynx. They are lined with a squamous stratified epithelium that often becomes so densely infiltrated by lymphocytes that it may be difficult to recognize. The lymphoid tissue in these tonsils forms a band that contains free lymphocytes and lymphoid nodules, generally with germinal centers. Each tonsil has 10–20 epithelial invaginations that penetrate the tonsil deeply, forming crypts, whose lumens contain desquamated epithelial cells, live and dead lymphocytes, and bacteria. Crypts may appear as purulent spots in tonsillitis. Separating the lymphoid tissue from subjacent structures is a band of dense connective tissue, the capsule of the tonsil. This capsule usually acts as a barrier against spreading tonsillar infections the numerous nodules that compromise the palatine tonsil. Lymph Nodules - spherical aggregations of lymphocytes that usually have germinal centers. Crypts - infoldings of the epithelium into the underlying connective tissue. Lymphocytes pass through the epithelium in areas of inflammation. Lymphocytes are seen in the lumen of some crypts. Sequestered crypts are usually inflamed and filled with debris and lymphocytes (pus). Plasma Cells - large numbers of plasma cells are usually seen in the underlying connective tissue near the epithelium.