Скачать с ютуб 8. QRS Complex - ECG assessment and ECG interpretation made easy в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно 8. QRS Complex - ECG assessment and ECG interpretation made easy в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно 8. QRS Complex - ECG assessment and ECG interpretation made easy или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон 8. QRS Complex - ECG assessment and ECG interpretation made easy в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
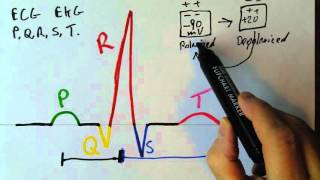
8. QRS Complex - ECG assessment and ECG interpretation made easy
📌𝗝𝗼𝗶𝗻 𝗢𝘂𝗿 𝗧𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗺 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹 𝗛𝗲𝗿𝗲:- https://t.me/bhanuprakashdr 📌 𝐅𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐨𝐧 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦:- / drgbhanuprakash 📌𝗦𝘂𝗯𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗯𝗲 𝗧𝗼 𝗠𝘆 𝗠𝗮𝗶𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗟𝗶𝘀𝘁:- https://linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash QRS Complex Morphology Main features to consider: Width of the complexes: Narrow versus broad. Voltage (height) of the complexes. Spot diagnoses: Specific morphology patterns that are important to recognise. QRS Width ------------------ Normal QRS width is 70-100 ms (a duration of 110 ms is sometimes observed in healthy subjects). The QRS width is useful in determining the origin of each QRS complex (e.g. sinus, atrial, junctional or ventricular). Narrow complexes (QRS less than 100 ms) are supraventricular in origin. Broad complexes (QRS greater than 100 ms) may be either ventricular in origin, or due to aberrant conduction of supraventricular complexes (e.g. due to bundle branch block, hyperkalaemia or sodium-channel blockade). Narrow QRS Complex Morphology ------------------------------------------------------- Narrow (supraventricular) complexes arise from three main places: Sino-atrial node (= normal P wave) Atria (= abnormal P wave / flutter wave / fibrillatory wave) AV node / junction (= either no P wave or an abnormal P wave with a PR interval less than 120 ms) Broad QRS Complex Morphology ----------------------------------------------------- Broad/Wide QRS Complexes A QRS duration greater than 100 ms is abnormal A QRS duration greater than 120 ms is required for the diagnosis of bundle branch block or ventricular rhythm Broad complexes may be ventricular in origin or due to aberrant conduction secondary to: Bundle branch block (RBBB or LBBB) Hyperkalaemia Poisoning with sodium-channel blocking agents (e.g. tricyclic antidepressants) Pre-excitation (i.e. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) Ventricular pacing Hypothermia Intermittent aberrancy (e.g. rate-related aberrancy) #qrscomplex #qrswave #qrsecg #ecgyoutube #ecgbasics #ecgcourse #ecgmadeeasy #ecgphysiology #ecgonline #completeecgcourse #ecginterpretation #narrowqrs #wideqrs #qrs #abnormalqrs #qrsduration